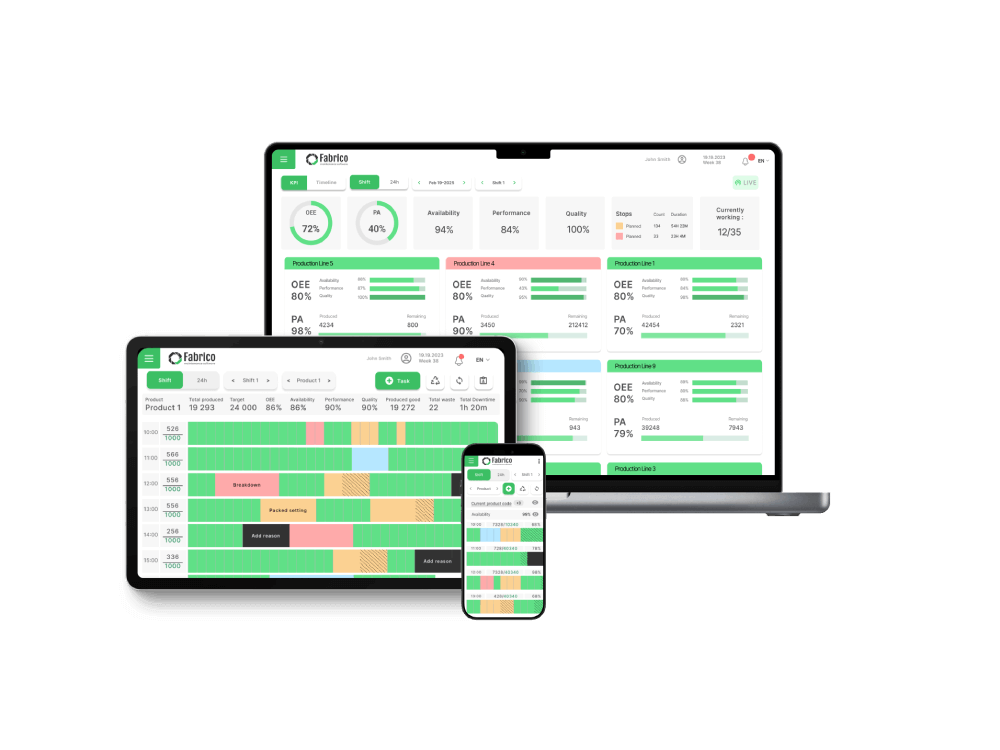
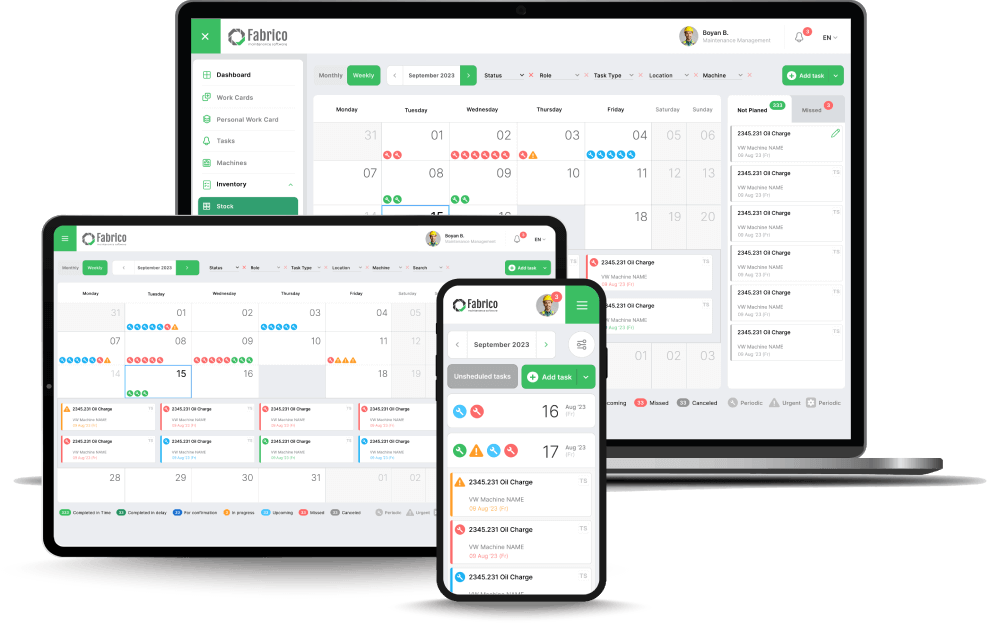
If you are wondering what the benefits of preventive maintenance are, you’ve come to the right place. Here are the top eight reasons why you should implement it in your organisation’s operations:
- Reduced downtimes
- Early malfunction detection
- Longer equipment lifespan
- Increased efficiency
- Fewer emergency situations
- Enhanced safety
- Cost savings
- Waste reduction
We will cover each one in more detail below. Let’s take a closer look.
1. Reduced downtimes
One of the first benefits of a preventive maintenance program is that it reduces downtime. Downtime is the period of time during which the machine in question stops working for maintenance or repair work. Sometimes, in manufacturing plants, there is an entire ecosystem of machines that work together to produce goods. However, when one machine breaks down and needs to be repaired, it can cause a domino effect on the remaining machines.
This can subsequently result in the entire plant being shut down for maintenance works. The consequences of this are lost productivity, lost labour hours and missed deadlines, among others. These challenges are overcome when implementing preventive maintenance. That’s because this maintenance method uses a proactive maintenance schedule.
Through this method, a maintenance team can be assigned to maintain a machine when the rest of the staff aren’t at the plant, during quieter production periods or others. This ensures the machines continue to function optimally and any potential mechanical faults are identified before they break down. Looking at maintenance history also helps teams improve a machine's performance. Therefore, preventive maintenance reduces costly downtime because it considers warning signs in advance before a fault actually occurs.
2. Early malfunction detection
The second advantage of a preventive maintenance service is the early detection of malfunctions. This is generally done when doing an in-depth inspection of a machine. It may require replacing a faulty part, lubricating machinery, performing examinations or other maintenance activities.
These activities can identify potential faults that may not be visible to the naked eye. By going deeper, a maintenance crew can prevent machine malfunctions much better. In fact, the numbers show that around 10% or less of industrial equipment wears out due to proper use. Based on this, the remaining 90% of machine failures are a result of preventable problems.
When a maintenance crew performs equipment observations and inspections, potential malfunctions can be detected and resolved. This principle applies to equipment disassembly and installation, too. And when your machines work properly, your organisational productivity improves. When compared to reactive maintenance, predictive maintenance emerges as the winner.
In our article on predictive maintenance challenges, you can learn more about early malfunction detection.
3. Longer equipment lifespan
Every machine has its own predetermined lifespan. Whether it’s meant to operate for two or seven years depends on the manufacturer. Manufacturers usually specify when their machines should be maintained for optimal performance and to prevent premature asset failure. A machine’s operational ability is extended when these guidelines are adhered to.
In such cases, organisations such as manufacturing plants can take advantage of greater productivity, efficiency and reliability. On the opposite side, if a machine is not maintained in time, even the most minor faults can add up over time, causing other more serious problems. However, when a machine is maintained proactively, maintenance crews can determine if a minor adjustment is necessary to prolong the machine’s lifespan.
In these scenarios, machines will require fewer calibrations and will run in a cleaner, more efficient way. In addition, knowing for how long you can realistically rely on your machines helps you better calculate their depreciation and when you should purchase a new replacement machine in the future.
Discover more about the impact on equipment lifespan in our article on total preventive maintenance.
4. Increased efficiency
The fourth important perk of a preventive maintenance plan is increased efficiency. Efficiency is when the right type of work gets done within a certain amount of time. When it comes to your machines, you know that your overall operations will take greater strain when there is a large breakdown that halts production.
However, with preventive maintenance, you can ensure that these large breakdowns are prevented. What’s more, when your machines run smoothly, you are also making more efficient use of your resources. For example, costs, allocation and use of lubricants, fuel, energy, water, spare parts and even labour hours can be reduced to ensure streamlined operations.
When this happens, you are much more likely to have greater production output, greater quality of products, more customer satisfaction and fewer missed deadlines. Your operations will ultimately run like a well-oiled machine as opposed to one that constantly faces hiccups and bottlenecks.
5. Fewer emergency situations
Among the benefits of planned preventative maintenance, your organisation will deal with fewer emergency situations and related work orders. It makes sense that when a machine is well-maintained on a schedule, it is less likely to break down.
However, the opposite—or reactive maintenance—deals with faults and breakdowns when they occur. These faults are usually major and require the machine to be pulled out of operation for a repair service to take place. Furthermore, organisations will need to immediately dispatch maintenance crews to the affected machine, meaning that they will be deviating from their current tasks.
As such, the productivity of these crews will be reduced when repairing an emergency breakdown. Another impact of this situation is that you are much more likely to require spare parts that may need to be shipped and managed on an express basis. This has obvious cost implications and can be considered a major financial leak.
6. Enhanced safety
We’ve all heard the expression “safety first”. While this may be true for many industries, it goes beyond being a priority for manufacturing plants. Instead, safety becomes a fundamental requirement. Safety is the absence of hazards and injuries. But it extends to so much more. The safety of your workforce should always be top of mind every single day your business operates. However, safety protocols must be put in place beforehand to ensure that your workers are protected from harm.
Unfortunately, you face this risk if your machines and assets are not maintained regularly. That’s where preventive measures must be taken and implemented to ensure that your staff is safe at all times. This can be done by choosing the right computerised maintenance management system (CMMS), which can help you predict and schedule maintenance. Catching potential faults in time and before they occur can help improve worker health and safety at your facility.
In addition to this, such a routine maintenance task can help your organisation remain compliant with regulatory requirements and help you pass your safety audits with flying colours. But when not implemented properly, equipment malfunctions, a frayed wire, overheating, halted functioning and more can endanger your staff. Emergency shutdown systems should also be maintained regularly and will only be used in the most extreme cases.
7. Cost savings
The next benefit of preventive maintenance that we will discuss is cost savings. This is a major factor for every organisation that operates in a competitive market. Businesses and manufacturing plants need to ensure that their expenses are kept as low as possible while revenue and profits are optimised. Often, there are investors as stakeholders who look at the business’s bottom line to determine whether they will invest more in the future.
When it comes to preventive maintenance, the business’s costs or expenses are reduced for several reasons. Firstly, catching a small issue quickly enough may mean that it can be resolved relatively simply without needing expensive spare parts. If spare parts are needed, this means that you will have them in your spare parts inventory, and you will not need to place urgent orders and deal with expensive overnight shipping.
Next, catching small problems on time and acting proactively means that you will not have to bring in an experienced maintenance crew. Relying on their expertise to fix the entire broken machine can be costly when compared to a small issue that your maintenance crew can catch and resolve. Other benefits of preventative maintenance include less downtime, which is costly. Reducing downtime can also result in significant savings. Overall, because it can be three to nine times more affordable to carry out preventive maintenance, this activity can be considered an investment in a company’s future.
In our article on preventive maintenance software for small companies, you can learn more about the contribution of such digital tools to cost-effectiveness and expense reduction.
8. Waste reduction
When a machine runs at optimal capacity, it is more efficient. When it’s more efficient, it is more likely to produce more high-quality goods. The opposite is also true. When a machine is not running optimally, it requires more spare parts, more consumables such as oil, grease, etc., electricity and water, and more manpower.
In addition, poorly operating machines slow down production. A result of this is that they can produce defective items of lower quality. These products are then discarded as they cannot be of any use. As such, organisations face significant wastage when their machines are not running at optimal capacity.
In the worst-case scenario, production can come to a complete halt and that affects the potential production of products. This can affect the organisation’s reputation for delivering on time. However, with preventive maintenance, machines operate optimally and consume materials with maximum efficiency. It’s also an important opportunity to detect defects at regular intervals. Furthermore, when a machine’s lifespan is optimised, it leads to prolonged activity and a longer period of time before the machine is scrapped.